
In this age of cybersecurity and digital identities, it’s sobering to know that according to a recent study by the Ponemon Institute, 81% of data breaches were caused by weak or stolen passwords. In light of such alarming statistics, can you imagine a world where passwords, those tricky combinations of letters, numbers, and symbols we’re always forgetting, become obsolete? Welcome to the future of authentication: Passwordless Authentication.
Passwordless Authentication is not a fad. It’s a proven solution to the password problem, and it’s about time we embraced it.
Cybersecurity Expert
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of this innovative security practice, uncovering its mechanisms, exploring its advantages, and investigating whether it stands a chance of becoming the new paradigm of digital security. Ready for a journey to a world without pesky passwords? Buckle up, as we’re just getting started.
1. Understanding Passwordless Authentication
In the ceaseless saga of digital evolution, one might ask, ‘What is passwordless authentication?’ As the name insinuates, passwordless authentication is a method of verifying identity without the need for lengthy, oft-forgotten passwords. Instead, it leverages other means of proof such as biometrics or physical devices. This indeed sounds promising, but what, one might wonder, led to the advent of such a system?
Consider the perennial issue with traditional passwords—they’re cumbersome, vulnerable, and not very user-friendly. Whether it’s the struggle to remember multiple complex passwords or the nagging fear of creeping cyberattacks, password woes are quite a headache. Thus, it was this bourgeoning desire for a safer and more intuitive approach to security that led to the birth of passwordless authentication.
So, how is it different? Well, instead of entering a password, users confirm their identity via other verification means such as a fingerprint scan, a secure token, or an email/SMS code. The user experience is thus not only improved but security is potentially enhanced as well—after all, it’s easier to steal a password than, say, a fingerprint or a cell phone. Interesting, isn’t it? But this is only the tip of the iceberg in understanding this revolutionary paradigm shift.
Keep in mind; that the journey toward understanding passwordless authentication is far from linear. It’s rife with intricate facts, compelling arguments, groundbreaking trends, and even a tinge of controversy. Are you ready to heed the call to adventure? Carry on reading as we tread deeper waters in the pursuit of understanding this fascinating concept.
2. Types of Passwordless Authentication
In your journey to understand passwordless authentication, you’ve surely wondered about the different types of this system, right? In our endeavor to appease this curiosity, we delve into the subject matter, illustrating the standard forms of passwordless authentication that are in common use (and a few that are, let’s say, less standard).
The premise of passwordless authentication, as you may recall, is to remove the necessity of inputting a password. Instead, other identifying factors are used. We all like to have options, and luckily, passwordless authentication comes in a few different flavors. Notably, there are three primary types, viz., biometric authentication, token-based authentication, and email/SMS-based authentication.
- Biometric Authentication: This method makes use of unique physical and biological traits of users to authenticate their identity. From the tip of your finger (fingerprint scanning) to the pattern of your iris (eye scanning), the sound of your voice (voice recognition) or even the way you type on a keyboard (behavioral biometrics), these traits can serve as your password. In a way, you might say that this method takes ‘being yourself’ to a new level.
- Token-based Authentication: Here, a one-time passcode (OTP) or a specific token generated by a security token device or software is used for the login process. In truth, it’s somewhat similar to getting an exclusive ‘fast pass’ every time you want to log in. It’s a one-time use and then – poof – it’s gone.
- Email/SMS-based Authentication: You guessed it – this type is dependent on a code sent to your email or mobile (via SMS) to facilitate access. It’s like verifying, “Yes! It’s me,” every time you seek access. Yet, like the token, this code is also for one-time use only.
Each of these methods, of course, has its own unique strengths and weaknesses (vulnerabilities in biometric systems? Sounds paradoxical, doesn’t it?). Before choosing a path to tread, it’s essential to understand the terrain. So, how exactly do biometric, token-based, and email/SMS-based authentication stack up against each other? Wouldn’t it be nice if there were a systematic comparison?
| Type | Strengths | Weaknesses |
| Biometric Authentication | High security, easy to use | Prone to privacy issues |
| Token-Based Authentication | Mobile, secure | Requires a physical device or software |
| Email/SMS-Based Authentication | User-friendly, widely accepted | Dependent on external networks |
Diving into these types in more detail should give you a more nuanced perspective of passwordless authentication. It’s like standing at a crossroads – each path leading to a different adventure (or in this case, a different form of authentication). So, which path piques your interest? After all, the choice of authentication method depends largely on your specific needs and concerns.
3. Advantages of Passwordless Authentication
Stepping into the terrain of passwordless authentication, you, as a user or maybe a security professional, might wonder what the fuss is all about. The advantages, you’ll discover, are manifold and we’ll disentangle them for you. Shall we proceed?
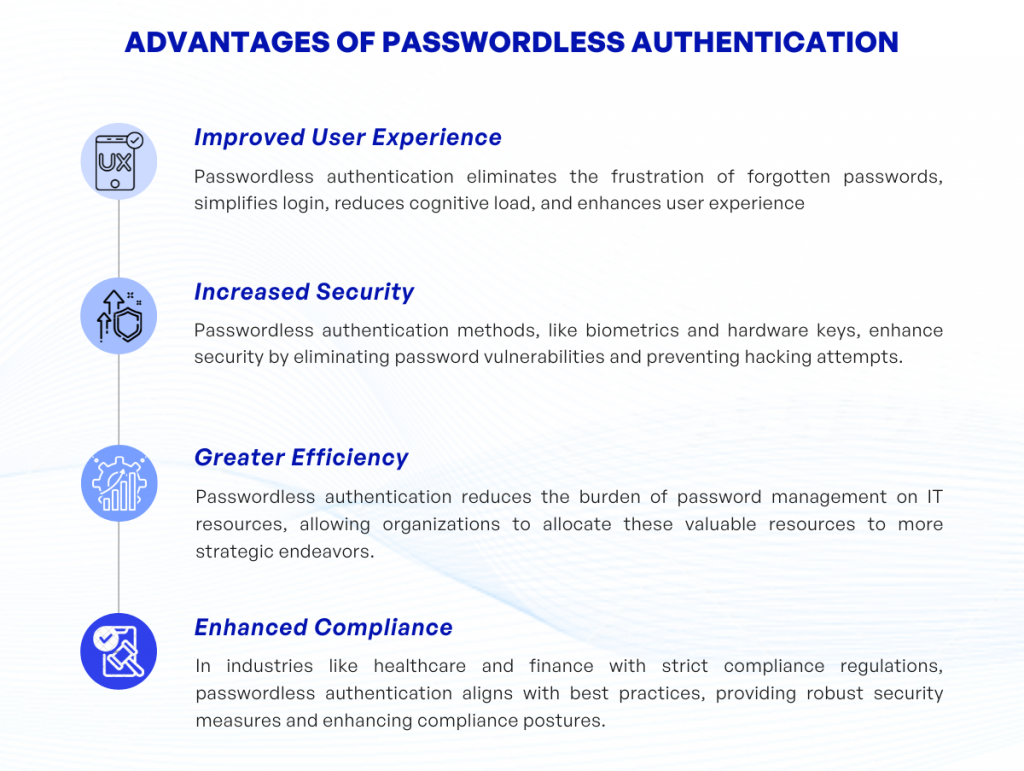
Improved User Experience: Have you ever been locked out of an account because you forgot your password? Quite frustrating, isn’t it? With passwordless authentication, this common irritant is eliminated. Passwords can be complex and often difficult to remember, especially when users maintain multiple accounts (which most of us do in today’s digitally fraught world). The passwordless approach simplifies the login process, reduces the cognitive load on users, and drastically improves the overall user experience.
Increased Security: Passwords can be easily cracked, guessed, or phished. They are a persistently weak link in the cyber security chain. However, passwordless authentication methods, like biometric data or hardware keys, aren’t susceptible to these age-old hacking tricks. Each user has unique physiological characteristics (in the case of biometrics), or a physical piece of equipment (as with hardware keys) which are exceedingly difficult for potential cybercriminals to replicate, thereby, increasing security.
Greater Efficiency: Password management consumes a significant portion of IT resources. This ranges from password reset requests, and managing password strength policies, to troubleshooting login concerns. By going passwordless, organizations can refocus these resources toward more strategic initiatives. An unintended but pleasant side-effect of passwordless authentication, perhaps?
Enhanced Compliance: Industries that handle sensitive information, such as healthcare and finance, are governed by stringent compliance regulations. One of the standard best practices includes strong authentication methods. Passwordless authentication fits the bill here, offering robust security checks and thus enhancing compliance postures.
Interweaving these insights, we can perceive how passwordless authentication paves a smoother, safer, and more efficient path in the digital arena. Quite impressive, isn’t it?
4. Disadvantages of Passwordless Authentication
It’s counterintuitive perhaps, but despite the clear advantages, passwordless authentication isn’t without its pitfalls. While convenience, security, and user experience are undoubtedly enhanced, in its stride toward digital evolution, passwordless authentication unwittingly opens a Pandora’s box of potential risks and drawbacks. Let’s turn our discerning eye toward some of the more significant concerns within this paradigm shift in the digital landscape.

1. Dependence on Single Devices: With passwordless authentication, a user’s device takes center stage as the key to accessing services. Sounds convenient, doesn’t it? But, have you ever wondered, what happens if the device is lost, stolen, or simply runs out of battery when needed the most? It can be a serious problem, immobilizing users from accessing their own services when they really need to.
2. Vulnerability to Phishing: Yes, passwordless doesn’t render you invulnerable to phishing. This is especially true for methods such as email or SMS-based authentication. In fact, phishing attempts can be even more successful because users may not be on guard for these types of attacks, since they don’t have a password to keep secret.
3. Risk of Server Breach: Passwordless authentication solutions can concentrate user credential data in a single point of failure—the server. If this is not sufficiently protected, it may potentially make the server an attractive target for hackers who are seeking to retrieve user’s credentials.
4. Ephemeral Challenges: Temporary, one-time authentication methods cause their own share of problems. For example, if an email link expires before a user clicks on it, they’re locked out. Also, what if the user doesn’t have immediate access to the secondary device or service (email, phone) to receive the link?
5. Privacy Concerns: While passwordless authentication methods notably improve upon traditional authentication mechanisms, they are not without privacy concerns. Biometric data can be misused if it falls into the wrong hands, or if the implementation doesn’t respect privacy boundaries.
In closing, as the saying goes: “There’s no such thing as a free lunch.” Passwordless authentication, while promising, is a double-edged sword. It’s essential to tread the pathway towards passwordless with eyes wide open, observing the nuances, understanding the pros and cons, and formulating a comprehensive strategy to implement it effectively and efficiently.
5. Use Cases
Passwordless authentication, being an innovative approach in the realm of digital security, finds its application across diverse industries and contexts. Indeed, one might pose the rhetorical question, “Where do we see passwordless authentication in effect?”.
To answer the aforementioned question, let’s explore a few scenarios:
1. Online Banking: Traditionally, online banking required customers to memorize complex passwords – an arduous feat for most. With the advent of passwordless authentication, however, banks can eliminate customer frustration, utilizing instead codes sent via SMS or email, or even biometric identifiers. This change not only simplifies the login process but also fortifies security safeguards, reducing the risk of password-based hacking. In a society where financial safety is paramount, this transition certainly signals progress.
2. E-commerce: In the bustling world of online shopping, users frequently abandon their shopping carts due to forgetfulness of their passwords. The implementation of passwordless authentication techniques, such as magic links or one-time passcodes (OTPs), simplifies this log-in process. This change inevitably leads to a surge in completed transactions, thereby fortifying the e-commerce market.
3. Workplace Security: Be it remote or in-office work, employees often grapple with remembering multiple passwords for various applications. Through passwordless authentication, this inconvenience is gradually phasing out. With options such as biometric authentication or hardware tokens, employees can focus more on productivity, and less on recalling an array of passwords.
Thus, these examples (while not exhaustive) illustrate the broad applicability and accelerating adoption of passwordless authentication. It’s important to note, however, that passwordless authentication does not yet have universal applicability. There are still instances where traditional password systems might be more suitable (due to a variety of factors including infrastructural limitations, transition barriers, or security requirements).
One could argue, though, that we are witnessing an evolutionary step in how we secure our digital experiences. Who knows? Perhaps a future where we no longer stress about securely storing, recalling, and regularly updating complex passwords isn’t that far off.
6. Conclusion: The Future of Authentication
As we navigate into the digital future, the trajectory of authentication methods certainly leans toward increasing sophistication and innovation. Passwordless authentication, as we’ve explored, offers promising solutions to the pitfall-ridden landscape of password-based security. Cracking the paradox of maintaining security while enhancing user experience, it beckons as an enticing option (albeit with its own set of challenges). Will it, then, dominate the future of authentication? Well, only time can reveal the complete panorama, but current trends seem to agree.
However, despite the many boons of passwordless authentication, it’s pertinent to highlight that no single solution can probably suffice to cater to the evolving threats in cyber security. Considering the dynamism of cyber threats, it’s essential to think of passwordless authentication as an important piece of the jigsaw puzzle, rather than the whole picture.
Integration of passwordless mechanisms with existing frameworks will require meticulous planning, continuous monitoring, and periodic evaluation—risk mitigation and user expediency will have to find a balanced meeting point. Do make sure that you explore, evaluate, and experiment before you jump onto the passwordless bandwagon; the transition has its own share of hurdles.
In the meantime, continue employing other forms of multi-factor authentication in conjunction with robust password policies until you’re ready to go fully passwordless. Remember, it’s a changing landscape, and flexibility is the ultimate key.
Consider this, dear reader: as we inch our way toward a digital society where convenience is king, we must be wary of sacrificing security on the altar of expediency. When considering the brass tacks, whether passwordless is indeed the next frontier in securing our data or simply a subsidiary cog in the authentication machinery remains to be seen. However, no matter what the front lines may shape up to be, the fundamental objective should always remain the same—adeptly protect what needs protection while making the process simpler for the user.
Indeed, the future of authentication is a fascinating topic, richer with each passing day as new technologies emerge and old ones evolve. Let’s keep an eye out for what’s next and embrace the changes with a mindset of learning, adapting, and securing. Who knows? You might be closer to the future than you realize.
If you have any questions about passwordless authentication, feel free to contact KVY TECH.


